Release Notes:
Measure Information Form
Version 2010B
**NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE**Measure Information Form
Measure Set: Acute Myocardial Infarction(AMI)
Set Measure ID: AMI-1
Performance Measure Name: Aspirin at Arrival
Description: Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients without aspirin contraindications who received aspirin within 24 hours before or after hospital arrival.
Rationale: The early use of aspirin in patients with acute myocardial infarction results in a significant reduction in adverse events and subsequent mortality. Aspirin therapy provides a percent reduction in mortality that is comparable to thrombolytic therapy and the combination provides additive benefit for patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (ISIS-2, 1988) and is also effective in patients with non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (Theroux, 1988 and RISC Group, 1990). National guidelines strongly recommend early aspirin for patients hospitalized with AMI (Antman, 2004). Despite these recommendations, aspirin remains under-utilized in eligible older patients hospitalized with AMI (Jencks, 2000).
Type of Measure: Process
Improvement Noted As: Increase in the rate
Numerator Statement: AMI patients who received aspirin within 24 hours before or after hospital arrival
Included Populations: Not applicable
Excluded Populations: None
Data Elements:
Denominator Statement: AMI patients without aspirin contraindications
Included Populations:
- Discharges with an ICD-9-CM Principal Diagnosis Code for AMI as defined in Appendix A, Table 1.1
Excluded Populations:
- Patients less than 18 years of age
- Patients who have a Length of Stay >120 days
- Patients with Comfort Measures Only documented on day of or day after arrival
- Patients enrolled in clinical trials
- Patients received as a transfer from an acute care facility where they were an inpatient or outpatient
- Patients received as a transfer from one distinct unit of the hospital to another distinct unit of the same hospital
- Patients received as a transfer from the emergency department of another hospital
- Patients discharged on day of arrival
- Patients discharged/transferred to another hospital for inpatient care on day of or day after arrival
- Patients who left against medical advice or discontinued care on day of or day after arrival
- Patients who expired on day of or day after arrival
- Patients discharged/transferred to a federal health care facility on day of or day after arrival
- Patients with one or more of the following aspirin contraindications/reasons for not prescribing aspirin documented in the medical record:
- Aspirin allergy
- Coumadin/warfarin as pre-arrival medication
- Other reasons documented by a physician/advanced practice nurse/physician assistant for not giving aspirin within 24 hours before or after hospital arrival
Data Elements:
Continuous Variable Statement:
Included Populations:
Excluded Populations:
Data Elements:
Risk Adjustment: No.
Data Collection Approach: Retrospective data sources for required data elements include administrative data and medical records.
Data Accuracy: Variation may exist in the assignment of ICD-9-CM codes; therefore, coding practices may require evaluation to ensure consistency.
Measure Analysis Suggestions: None
Sampling: Yes. For additional information see the Sampling Section.
Data Reported As: Aggregate rate generated from count data reported as a proportion.
Selected References:
- Anderson JL, Adams CD, Antman EM, Bridges CR, Califf RM, Casey DE Jr, Chavey WE II, Fesmire FM, Hochman JS, Levin TN, Lincoff AM, Peterson ED, Theroux P, Wenger NK, Wright RS. ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non–ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2002 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unstable Angina/Non–ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction): developed in collaboration with the American College of Emergency Physicians, American College of Physicians, Society for Academic Emergency Medicine, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;50:e1–157.
- Antman EM, Anbe DT, Armstrong PW, Bates ER, Green LA, Hand M, Hochman JS, Krumholz HM, Kushner FG, Lamas GA, Mullany CJ, Ornato JP, Pearle DL, Sloan MA, Smith SC Jr. ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee to Revise the 1999 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction). 2004.
- Krumholz HM, Anderson JL, Brooks NH, Fesmir FM, Lambrew CT, Landrum MB, Weaver WD, Whyte J. ACC/AHA Clinical Performance Measures for Adults With ST-Elevation and Non–ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: a report of the ACC/AHA Task Force on Performance Measures (ST-Elevation and Non–ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Performance Measures Writing Committee). J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:236–65. Available at http://www.acc.org and http://www.americanheart.org.
- Randomized trial of intravenous streptokinase, oral aspirin, both or neither among 17,187 cases of suspected acute myocardial infarction: ISIS-2. ISIS-2 (Second International Study of Infarct Survival) Collaborative Group. Lancet. 1988 Aug 13;2(8607):349-60.
- Jencks SJ, Cuerdon T, Burwen DR, Fleming B, Houck PM, Kussmaul AE, Nilasena DS, Ordin DL, Arday DR. Quality of medical care delivered to Medicare beneficiaries: a profile at state and national levels. JAMA. 2000;284:1670-1676.
- Risk of myocardial infarction and death during treatment with low dose aspirin and intravenous heparin in men with unstable coronary artery disease. The RISC Group. Lancet 1990; 336(8719):827-830.
- Theroux P, Ouimet H, McCans J et al. Aspirin, heparin, or both to treat acute unstable angina. N Engl J Med 1988; 319(17):1105-1111.
Measure Algorithm:
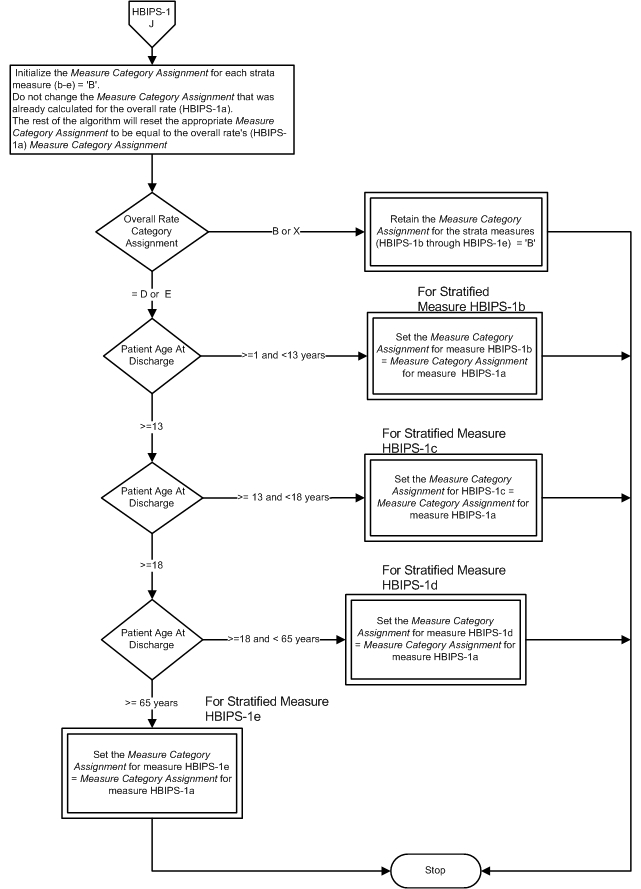
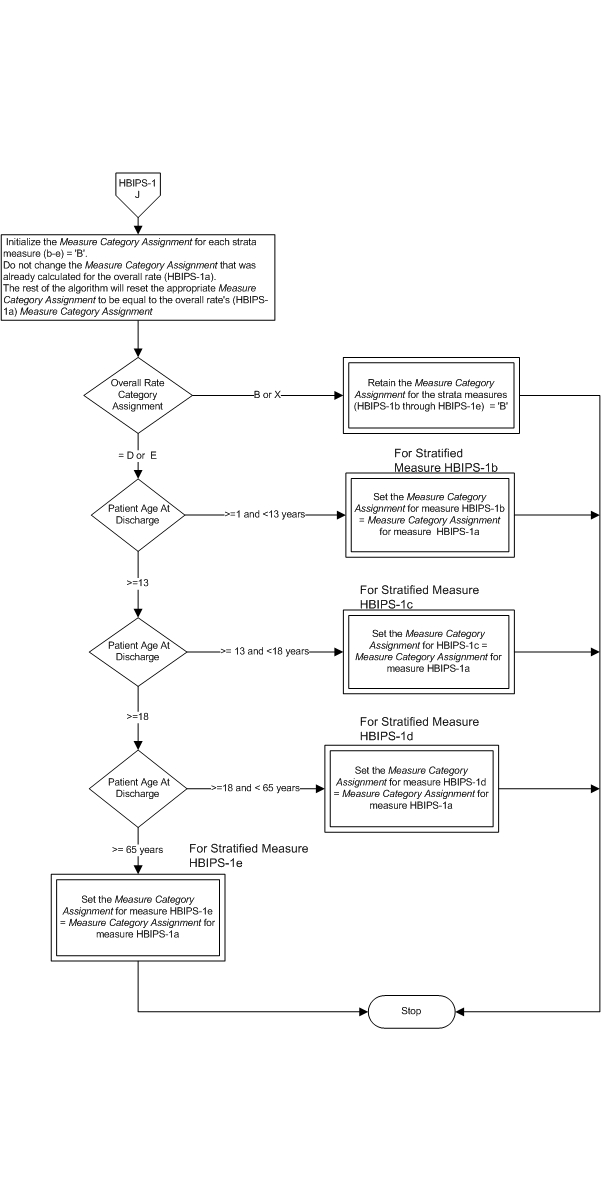
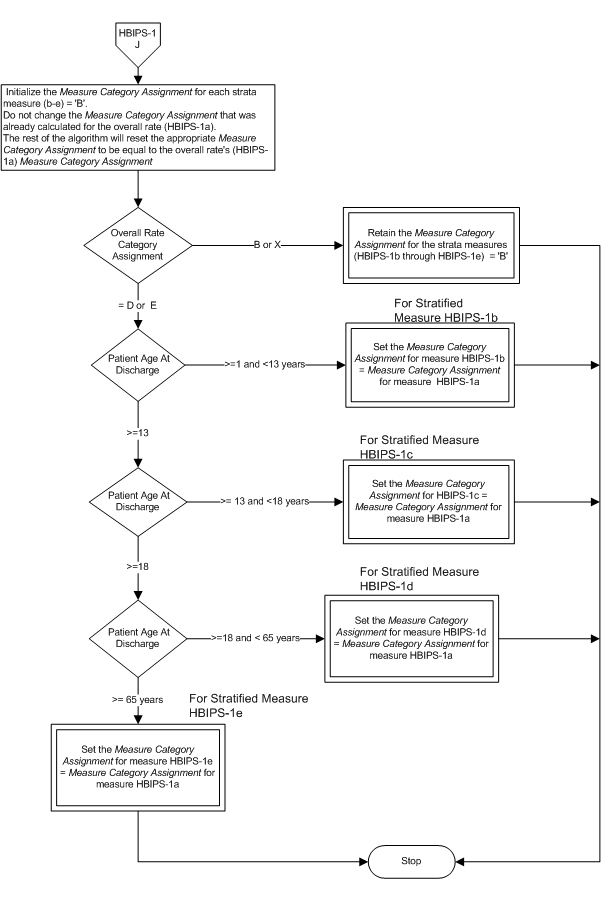
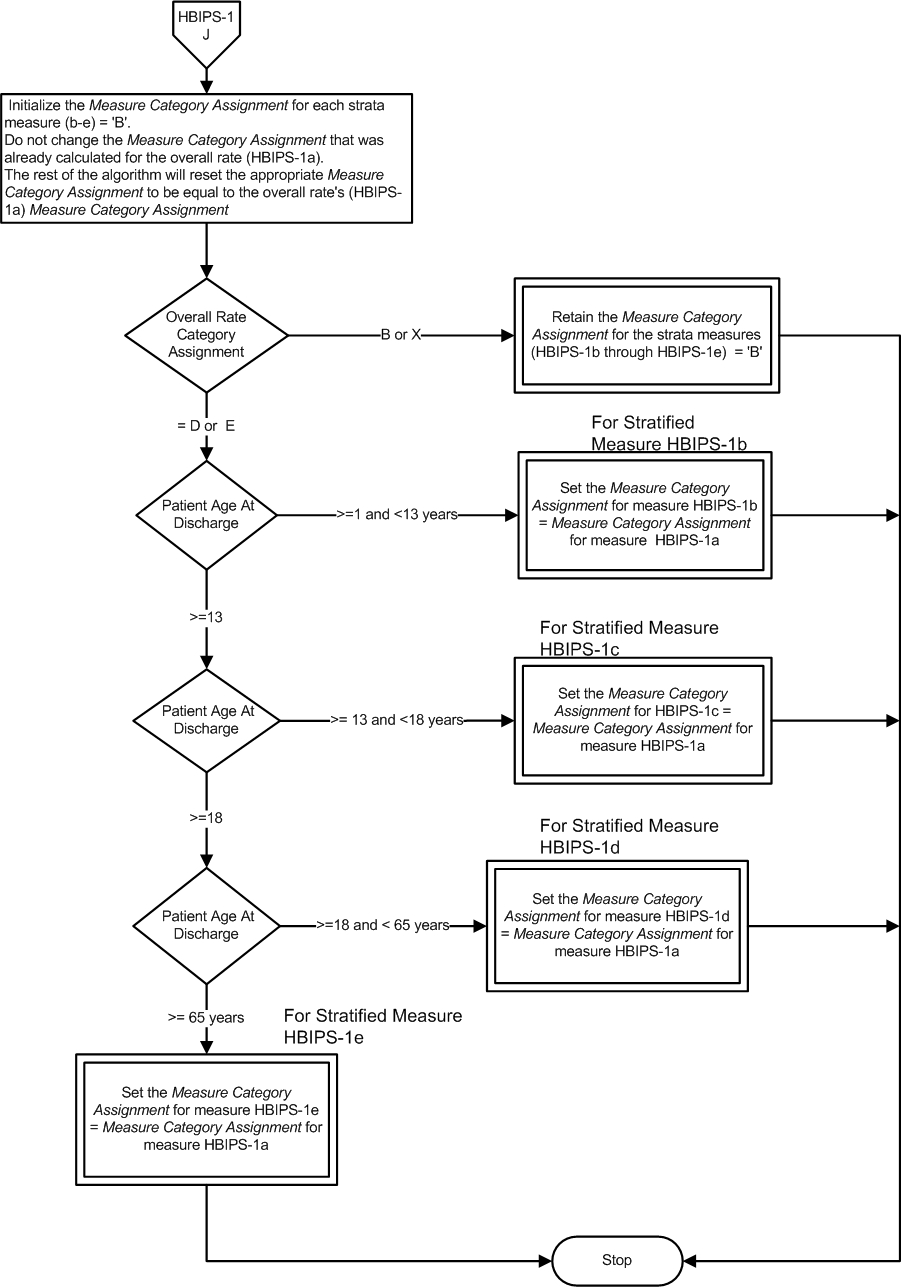
 Attach file Attach file
|
Measure Information Form AMI-1
Specifications Manual for Joint Commission National Quality Core Measures (2010B)
Discharges 10-01-10 (4Q10) through 03-31-11 (1Q11)
|
|
|




 Attach file
Attach file