Release Notes:
Sampling Chapter
Version 2010B
Population and Sampling Specifications
Introduction
Population
Defining the population is the first step to estimate a hospital’s performance. A population is generally defined as a collection of patients sharing a common set of universally measured characteristics, such as an ICD-9-CM Principal Diagnosis or Procedure Code. The Initial Patient Population and diagnosis codes meet this description for the national quality measures. For the purpose of measuring national quality measures, the term “Initial Patient Population” is defined below:
- An “Initial Patient Population” refers to all patients (Medicare and non-Medicare) who share a common set of specified, administratively derived data elements, with a length of stay less than or equal to 120 days (Admission Date – Discharge Date ≤ 120 days). This may include ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes or other population characteristics such as age. For example, the population for the Surgical Care Improvement Project SCIP-Inf-1, 2, and 3 measures include all patients with an ICD-9-CM Principal Procedure Code as defined in Appendix A, Tables 5.01 through 5.08 and a Patient Age (Admission Date – Birthdate ≥ 18 years).
Cases identified as being in the Initial Patient Population for the measure set, strata (e.g., SCIP), or sub-population (e.g., Pregnancy) are eligible to be sampled. For the definition of the Initial Patient Population(s) for each measure set, refer to the appropriate Initial Patient Population discussion in the Measure Information section of this manual.
Sampling
Sampling is a process of selecting a representative part of a population in order to estimate the hospital’s performance, without collecting data for its entire population. Using a statistically valid sample, a hospital can measure its performance in an effective and efficient manner. Sampling is a particularly useful technique for performance measures that require primary data collection from a source such as the medical record. Sampling should not be used unless the hospital has a large number of cases in the Initial Patient Population because a fairly large number of sample cases are needed to achieve a representative sample of the population. For the purpose of sampling national quality measures, the terms “sample”, “effective sample”, and “case” are defined as below:
- The “sample” is the fraction of the population that is selected for further study.
- “Effective sample” refers to that part of the sample that makes it into the denominator of a measure. This is defined as the sample for a measure minus all the exclusions and contraindications for that measure in that sample.
- A “case” refers to a single record (or an episode of care [EOC]) within the population. For example, during the first quarter a hospital may have 100 patients who had a principal surgery associated to the SCIP-Inf-1, 2, and 3 measures. The hospital’s Initial Patient Population would include 100 cases or 100 patient records for these measures during the first quarter.
To obtain statistically valid sample data, the sample size should be carefully determined and the sample cases should be randomly selected in such a way that the individual cases in the population have an equal chance of being selected. Only when the sample data truly represent the whole population can the sample-based performance measure data be meaningful and useful.
Each hospital is ultimately responsible that sampling techniques applied for their hospital adhere to the sampling requirements outlined in this manual. Performance measurement systems are responsible for ensuring that the sampling techniques are applied consistently across their client hospitals.
Sampling is done by national quality measure set, except for Children’s Asthma Care (CAC), Pregnancy (PR), and Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP), which are done by strata or sub-population respectively. For measures requiring medical record abstraction, sampling must be done using available databases that contain all discharges for the transmission quarter.
Note:
Hospitals are NOT required to sample their data. For measure sets that can be derived entirely from administrative data (such as the PR set), it may be simpler to submit all cases. Similarly, if sampling offers minimal benefit (i.e., a hospital has 80 cases for the quarter and must select a sample of 76 cases) the hospital may choose to use all cases.
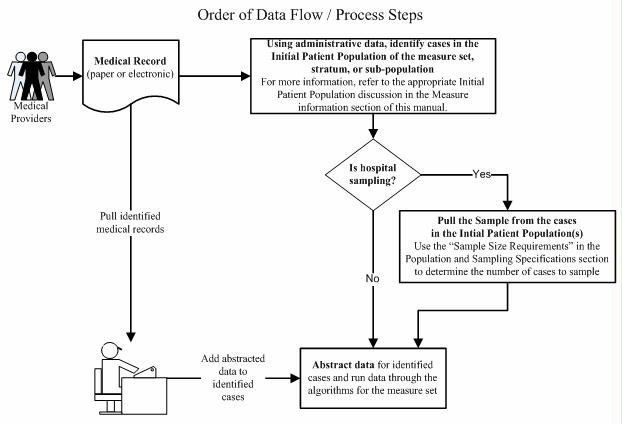
Order of Data Flow
Each measure set or strata have a unique definition of Initial Patient Population and sample size requirement. However, the same data flow or process steps can be used to identify the data that is transmitted to the QIO Clinical warehouse and the Joint Commission’s Data Warehouse. These process steps are:
- First, identify the Initial Patient Population for the measure set. An Initial Patient Population is defined for each measure set, stratum, and sub-population and the count is collected in the Initial Patient Population Size data elements. This data pull utilizes administrative data such as ICD-9-CM diagnosis and procedure codes, Admission Date, and Birthdate. All ICD-9-CM diagnosis and procedure codes included in the appropriate Initial Patient Population definition must be applied. This identification process must be completed prior to the application of data integrity filter, measure exclusions, and the application of sampling methodology. For specific measure set, stratum, and sub-population definitions, refer to the appropriate Initial Patient Population discussion in the Measure Information section of this manual.
- Second, if the hospital is sampling, use the Initial Patient Population identified above and pull the sample of medical records for each measure set, stratum, or sub-population using the Sample Size Requirements defined in the appropriate Measure Information section of this manual.
- Third, collect or abstract from the identified medical records the general and measure specific data elements that are needed for the measure set. The count of the number of cases used in this step is collected in the Sample Size data elements.
- If the hospital is not sampling, use the medical records identified in the first data pull.
- If the hospital is sampling, use the medical records from the cases in the identified sample.
Sample Size Requirements
Hospitals that choose to sample have the option of sampling quarterly or sampling monthly. The sample size requirements for each of these options are described in turn. Hospitals need to use the next highest whole number when determining their required sample size. See below for rounding examples. For each measure sets sample size requirements, refer to the appropriate measure set’s Measure Information section in this manual.
Hospitals selecting sample cases for measure sets that are not stratified (e.g., AMI and PN) must ensure that its Initial Patient Population(s) and effective sample size(s) meet the conditions stated in the measure set’s Sample Size Requirements.
For hospitals selecting sample cases for stratified measure sets or measure sets with sub-populations (e.g., SCIP and PR), a modified sampling procedure is required. Hospitals selecting sample cases for these sets must ensure that each individual stratum’s population/sub-population and effective sample size meets the conditions stated in the measure set’s Sample Size Requirements.
Regardless of the option used, hospital samples must be monitored to ensure that sampling procedures consistently produce statistically valid and useful data. Because the sample for a measure set will rarely be equal to the effective sample due to exclusions and contraindications, hospitals selecting sample cases MUST submit AT LEAST the minimum required sample size. The sample size tables for each option automatically build the number of cases needed to obtain the required sample sizes.
Hospitals that sample, should sample by their Medicare Provider ID. For most organizations, there is a one to one correspondence between their Medicare Provider ID and the Joint Commission’s Health Care Organization Identifier. Sampling by Medicare Provider ID may cause those organizations that have chosen to be accredited such that they have multiple Medicare Provider ID combined under one Health Care Organization Identifier to over sample from the Joint Commission’s perspective. Organizations reporting data to CMS must sample at the level of the individual Medicare Provider ID. All data that are sampled (by Provider ID) must be transmitted to both CMS and The Joint Commission.
A hospital may choose to use a larger sample size than is required. Hospitals whose Initial Patient Population size is less than the minimum number of cases per quarter/month for the measure set, stratum, or sub-population, cannot sample. Refer to the Sample Size Requirement tables provided in each measure set’s Measure Information section to determine the minimum number of cases that need to be sampled for each population.
Quarterly Sampling Examples
Quarterly Example 1: Measure set is Not Stratified
Hospitals selecting sample cases for measure set ABC, which is not stratified, must ensure that its Initial Patient Population and effective quarterly sample size meet the following conditions:
- The effective quarterly sample size for a measure set is at least 35 cases per quarter; and
- The required quarterly sample size is at least 20% of the Initial Patient Population.
Quarterly Sample Size
Based on Initial Patient Population for the ABC Measure Set
Examples
- A hospital’s ABC Initial Patient Population is 77 patients during the first quarter. Using the above table, no sampling is allowed – 100% of the population is required.
- A hospital’s ABC Initial Patient Population is 100 patients during the second quarter. Using the above table, the required sample size is seen to be a minimum of 78 ABC patients for this quarter.
- A hospital’s ABC Initial Patient Population is 401 patients during the third quarter. Using the above table, the required sample size is seen to be 20% of the population, or 81 cases for the quarter (twenty percent of 401 equals 80.2 rounded to the next whole number = 81).
- A hospital’s ABC Initial Patient Population is 1551 patients during the fourth quarter. Using the above table, the required sample size is seen to be a minimum of 311 ABC patients for this quarter.
Quarterly Example 2: Measure set is stratified
For hospitals selecting sample cases for measure set XYZ which contains 8 strata, a modified sampling procedure is required. Hospitals selecting sample cases for these sets must ensure that each individual stratum’s population and effective quarterly sample size meets the following conditions.
- Select within each of the seven individual measure stratum and the 8th XYZ stratum. The effective quarterly sample size within a stratum is at least 16 cases per quarter.
- The required quarterly sample size is at least 10% of the stratum population.
Quarterly Sample Size
Based on Initial Patient Population for the XYZ Measure Set
Example
- The SCIP Initial Patient Population sizes for a hospital is 5, 50, 15, 140, 35, 201, 3, and 481 patients respectively per quarter. The required quarterly sample sizes would be 5, 16, 15, 16, 16, 21, 3, and 48.
- The 1st, 3rd, and 7th strata are less than the minimum required quarterly sample size, so 100% of each of these strata are sampled.
- The 2nd, 4th, and 5th strata each require 16 cases to be sampled.
- The 6th stratum has 201 patients per quarter, which requires a 10% sample size, or 21 cases (twenty percent of 201 equals 20.1 rounded to the next whole number = 21).
- The 8th stratum is more than the maximum required quarterly sample size, so this stratum requires 48 cases to be sampled.
Monthly Sampling Examples
Monthly Example 1: Measure set is Not Stratified
Hospitals selecting sample cases for ABC measure set must ensure that its Initial Patient Population and effective monthly sample size meet the following conditions:
- The effective monthly sample size for a measure set is at least 12 cases per month; and
- The required monthly sample size is at least 20% of the Initial Patient Population.
Monthly Sample Size
Based on Initial Patient Population for the ABC Measure Set
Examples
- A hospital’s ABC Initial Patient Population is 25 patients during January. Using the above table, no sampling is allowed – 100% of the population is required.
- A hospital’s ABC Initial Patient Population is 130 patients during February. Using the above table, the required sample size is seen to be a minimum of 26 ABC patients for this month.
- A hospital’s ABC Initial Patient Population is 301 patients during March. Using the above table, the required sample size is seen to be 20% of the population, or 61 cases for the month (twenty percent of 301 equals = 60.2 rounded to the next whole number = 61.
- A hospital’s ABC Initial Patient Population is 516 patients during April. Using the above table, the required sample size is seen to be a minimum of 104 ABC patients for this month.
Monthly Example 2: Measure set is Stratified
For hospitals selecting sample cases for the XYZ measure set, a modified sampling procedure is required. Hospitals selecting sample cases for this set must ensure that each individual strata population and effective monthly sample size meets the following conditions:
- Select within each of the seven individual measure stratum and the 8th XYZ stratum. The effective monthly sample size within a stratum is at least 6 cases per month.
- The required monthly sample size is at least 10% of the strata population.
Monthly Sample Size
Based on Initial Patient Population for the XYZ Measure Set
Example
- The SCIP Initial Patient Population sizes for a hospital is 5, 50, 15, 141, 35, 201, 3, and 481 patients respectively in June. The required monthly sample sizes would be 5, 6, 6, 15, 6, 16, 3, and 16.
- The 1st and 7th strata are less than the minimum required monthly sample size, so 100% of each of these strata are sampled.
- The 2nd, 3rd, and 5th strata each require 6 cases to be sampled.
- The 4th stratum has 141 patients per month, which requires a 10% sample size, or 15 cases (twenty percent of 141 equals 14.1 rounded to the next whole number = 15).
- The 6th and 8th strata are each more than the maximum required monthly sample size, so this stratum requires 16 cases to be sampled.
Sampling Approaches
As previously stated in this section, hospitals have the option to sample from their population, or submit their entire population. Hospitals that choose to sample must ensure that the sampled data represent their Initial Patient Population by using either the simple random sampling or systematic random sampling methods and that the sampling techniques are applied consistently within a quarter. For example, monthly samples for a measure set, stratum, or sub-population must use consistent sampling techniques across the quarterly submission period.
- Simple random sampling - selecting a sample size (n) from a population of size (N) in such a way that every case has the same chance of being selected.
- Systematic random sampling - selecting every kth record from a population of size N in such a way that a sample size of n is obtained, where k ≤ N/n. The first sample record (i.e., the starting point) must be randomly selected before taking every kth record. This is a two-step process: a) Randomly select the starting point by choosing a number between one and k using a table of random numbers or a computer-generated random number; and a) Then select every kth record thereafter until the selection of the sample size is completed.
Each hospital is ultimately responsible that sampling techniques applied for their hospital adhere to the sampling requirements outlined in this manual. Performance measurement systems are responsible for ensuring that the sampling techniques are applied consistently across their client hospitals.
Sampling Approach Examples
For a hospital with an Initial Patient Population size of 350 ABC measure set discharges per quarter, the sample size would be 78. To select a random sample of 78 ABC patients:
- Simple random sampling:
- Generate random numbers for individual ABC patient records from a random number function using a statistical software package or computer programming language.
- Sort data by the random numbers either in an increasing or decreasing order.
- Select the first 78 ABC patient records as the random sample.
- Systematic random sampling:
- In this example, the hospital’s Initial Patient Population size= 350 and the sample size = 78. Divide the Initial Patient Population size by the sample size and take the quotient (i.e., the integer portion) as the sampling interval k. The sampling interval k = 350/78 = 4.5. Thus, every 4th ABC patient record will be selected from the Initial Patient Population until 78 cases are selected.
- To ensure that each ABC patient has an equal chance of being selected, the “starting point” must be randomly determined before selecting every 4th ABC patient record. This can be done using a computer random number generator or a random number table to randomly choose a number between 1 and 4 as the starting point.
Transmission of Initial Patient Population and Sample Data Elements
CMS and The Joint Commission requires transmission of Initial Patient Population and sample count data. Transmission of Initial Patient Population and sample count data elements are used to assist in evaluating completeness of submission in accordance with CMS/The Joint Commission sampling requirements.
The Initial Patient Population Size refers to all patients (Medicare and non-Medicare) who share common payment sources which can be identified by utilizing administrative data such as the UB-04. All ICD-9-CM diagnosis and procedure codes included in the appropriate Initial Patient Population definition must be applied. This identification process must be completed prior to the application of data integrity filter, measure exclusions, and the application of sampling methodology. For specific measure set and strata definitions, refer to the appropriate Initial Patient Population discussion in the Measure Information section of this manual.
The Initial Patient Population and sample data elements are:
- ICD Population Size *
- Initial Patient Population Size – Medicare Only **
- Initial Patient Population Size – Non-Medicare Only **
- Sample *
- Sampling Frequency **
- Sample Size – Medicare Only **
- Sample Size – Non-Medicare Only **
Sample indicates whether or not the hospital has sampled data for the specified time period.
Sampling Frequency indicates if the hospital has sampled using the monthly or quarterly methodology, or whether the entire population was used for the specified time period.
Initial Patient Population Size – Medicare Only includes all patients that are billed under Medicare or Title 18. Medicare can be listed as a primary, secondary, tertiary or lower on the list of payment sources for the patient. In addition, patients who are participating as a member of a Medicare HMO/Medicare Advantage are included in the Medicare counts, e.g., Medicare Blue, Humana gold, Secure Horizons, AARP, Coventry Advantra, etc.
* The Joint Commission: Transmitted in the aggregate data file. Refer to the
ORYX Technical Implementation Guide for more information.
CMS: Not transmitted to CMS.
** The Joint Commission and CMS: Transmitted in the Hospital Initial Patient Population data file. Refer to the
Hospital Initial Patient Population Data XML File Layout in the Transmission section of this manual.
*** The Joint Commission: Transmitted in the aggregate data file. Refer to the
ORYX Technical Implementation Guide for more information.
CMS: Transmitted in the Hospital Clinical Data file. Refer to the
Hospital Clinical Data XML File Layout in the Transmission section of this manual.
Initial Patient Population and Sample Size Examples
Example 1 – Hospital does not sample
A hospital uses the Initial Patient Population(s) for the ABC measure set to identify 120 cases in the ABC Initial Patient Population during the second quarter. The hospital does not sample the ABC measure set, so data for all 120 cases are collected and used to calculate the hospital’s rate for each ABC measure. 40 of the 120 cases in the ABC Initial Patient Population are Medicare patients.
The breakdown of data by month and Medicare / Non-Medicare is:
The following is transmitted for each month in the quarter:
Example 2 – Hospital samples monthly
A hospital uses the Initial Patient Population(s) for the ABC measure set to identify 120 cases in the ABC Initial Patient Population during the second quarter. From these 120 cases, the hospital uses the monthly sample size requirements and randomly selects a sample of 26 cases for each month. Data for these 26 cases are collected and used to calculate the hospital’s rate for each ABC measure. 40 of the 120 cases in the ABC Initial Patient Population are Medicare patients and 24 of these cases were included in the sample.
The breakdown of data by month and Medicare / Non-Medicare is:
The following is transmitted for each month in the quarter:
Example 3 – Hospital samples quarterly
A hospital uses the Initial Patient Population(s) for the ABC measure set to identify 120 cases in the ABC Initial Patient Population during the second quarter. From these 120 cases, the hospital uses the quarterly sample size requirements and randomly selects a sample of 78 cases. Data for these 78 cases are collected and are then used to calculate the hospital’s rate for each ABC measure. 40 of the 120 cases in the ABC Initial Patient Population are Medicare patients and 20 of these cases were included in the sample.
The breakdown of data by month and Medicare / Non-Medicare is:
The following is transmitted for each month in the quarter:
Related Topics
