Measure Information Form
Version 2020A
Palliative Care (PAL)
Set Measures
| Set Measure ID | Measure Short Name |
|---|---|
| PAL-01 | Pain Screening |
| PAL-02 | Pain Assessment |
| PAL-03 | Dyspnea Screening |
| PAL-04 | Treatment Preferences and Goals of Care |
| PAL-05 | Treatment Preferences Discharge Document |
General Data Elements
| Element Name | Collected For |
|---|---|
| Admission Date | All Records, |
| Birthdate | All Records, |
| Discharge Date | All Records, Not collected for HBIPS-2 and HBIPS-3 |
| Sex | All Records, |
Measure Set Specific Data Elements
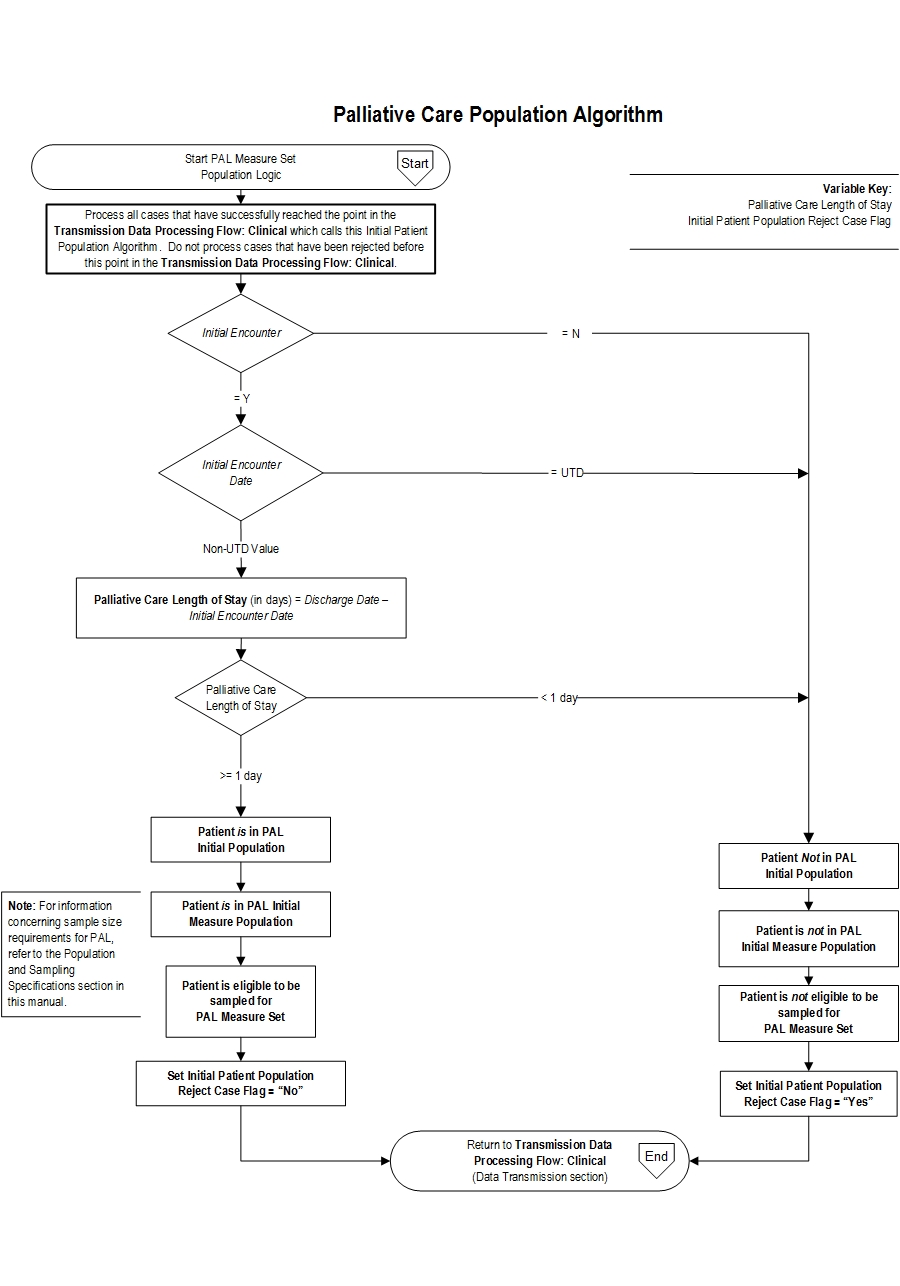
Palliative Care (PAL) Initial Patient Population
The PAL Measure Set Population (common to all PAL measures) is defined as all patients who have received a consultation with any member of the palliative care service team. “Consultation” indicates that the patient received a face to face encounter visit with any member of the palliative care core interdisciplinary team. The core interdisciplinary team is comprised of the following: Physician(s); Registered nurse(s) or advanced practice nurse(s); Chaplain(s) or, spiritual care professional(s); Social worker(s). The population of the PAL measure set can be identified by using data elements that are common to all of the performance measures in the set:- Discharge Date
- Initial Encounter
- Admission Date
- Birthdate
- Sex
Note – General Data Elements:
The following General Data Elements are optional for the PAL measure set. Collection of these data elements is not currently required for the identification of the initial patient population or the calculation of the measures for purposes of measure submission for certification. Optional General Data Elements:- Hispanic Ethnicity
- ICD-10-CM Other Diagnosis Codes
- ICD-10-CM Principal Diagnosis Code
- ICD-10-PCS Other Procedure Codes
- ICD-10-PCS Principal Procedure Code
- Payment Source
- Postal Code
- Race
Initial Patient Population Algorithm
Sampling / Sample Size Requirements
Sampling MethodologySampling is a process of selecting a representative part of a population to estimate the organization’s performance without collecting data for its entire population. Using a statistically valid sample, an organization can measure its performance in an effective and efficient manner. Sampling is a particularly useful technique for performance measures that require primary data collection from a source, such as the medical record. Sampling should not be used unless the organization has a large number of cases in the measure population, because a fairly large number of sample cases is needed to achieve a representative sample of the population of interest. To obtain statistically valid sample data, the sample size should be carefully determined, and the sample cases should be randomly selected in such a way that the individual cases in the population have an equal chance of being selected. Only when the sample data truly represent the whole population can the sample-based performance measure data be meaningful and useful.
Sampling ApproachesSimple random sampling - selecting a sample size (n) from a population of size (N) in such a way that every case has the same chance of being selected. Systematic random sampling - selecting every kth record from a population of size N in such a way that a sample size of n is obtained, where k ≤ N/n. The first sample record (i.e., the starting point) must be randomly selected before taking every kth record. This is a two-step process: a) Randomly select the starting point by choosing a number between one and k using a table of random numbers or a computer-generated random number; and b) Then select every kth record thereafter until the selection of the sample size is completed. As an example, say the site has 33 cases for the month. These 33 cases would then be put on a list and numbered from 1 to 33. First we calculate the sampling interval k as 33/10 which rounds to 3. The site would then randomly choose a number between 1 and 3 to use as the starting point on the list, sample this case, and then from this point sample every 3rd case on the list until they come to the end of the list to create their sample.
| Monthly Patient Volume (number of discharges)” |
Monthly Sample Size (number of medical records) |
|---|---|
| 1 - 9 | 100% |
| 10 - 49 | 10 cases |
| 50 - 99 | 20% |
| => 100 | 20 cases |
CPT® only copyright 2019 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. CPT® is a registered trademark of the American Medical Association.
You, your employees and agents are authorized to use CPT® only as contained in The Joint Commission performance measures solely for your own personal use in directly participating in healthcare programs administered by The Joint Commission. You acknowledge that the American Medical Association (“AMA”) holds all copyright, trademark and other rights in CPT®.
Any use not authorized herein is prohibited, including by way of illustration and not by way of limitation, making copies of CPT® for resale and/or license, transferring copies of CPT® to any party not bound by this Agreement, creating any modified or derivative work of CPT®, or making any commercial use of CPT®. License to use CPT® for any use not authorized herein must be obtained through the American Medical Association, Intellectual Property Services, AMA Plaza, 330 North Wabash Avenue, Suite 39300, Chicago, Illinois 60611-5885. Applications are available at the American Medical Association Web site, www.ama- assn.org/go/cpt.
U.S. Government Rights This product includes CPT® which is commercial technical data, which was developed exclusively at private expense by the American Medical Association, 330 North Wabash Avenue, Chicago, Illinois 60611. The American Medical Association does not agree to license CPT® to the Federal Government based on the license in FAR 52.227-14 (Data Rights - General) and DFARS 252.227-7015 (Technical Data - Commercial Items) or any other license provision. The American Medical Association reserves all rights to approve any license with any Federal agency.
Disclaimer of Warranties and Liabilities. CPT® is provided “as is” without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the AMA, are not part of CPT®, and the (AMA is not recommending their use. The AMA does not directly or indirectly practice medicine or dispense medical services. The responsibility for the content of this product is with The Joint Commission, and no endorsement by the AMA is intended or implied. The AMA disclaims responsibility for any consequences or liability attributable to or related to any use, non-use, or interpretation of information contained or not contained in this product.
This Agreement will terminate upon notice if you violate its terms. The AMA is a third party beneficiary to this Agreement.
Should the foregoing terms and conditions be acceptable to you, please indicate your agreement and acceptance by clicking below on the button labeled “accept”.