Measure Information Form
Version 2024B
Measure Information Form
Seclusion or restraint should be initiated only when less restrictive measures have proven ineffective, and the behavioral emergency poses serious and imminent danger to the person, staff, or others. Such interventions should be discontinued as soon as the behavioral criteria for release has been met, and never used as punishment (APNA, 2022).
Providers should first attempt verbal de-escalation, and establish clear protocols to guide decision-making for the initiation and removal of restraint and seclusion (APA, 2022).
Type Of Measure: Process Improvement Noted As: Decrease in the rateNumerator Basis: The numerator evaluates the number of hours of physical restraint; however, the algorithm calculates the number of minutes to ensure a more accurate calculation of the measure. Convert the minutes to hours when analyzing and reporting this measure.
Included Populations:Denominator Statement: Number of psychiatric inpatient daysExcluded Populations: None Data Elements:
- Patients for whom at least one physical restraint event is reported during the month
Denominator Basis: per 1,000 hours
Included Populations:Excluded Populations:
- All psychiatric inpatient days
Data Elements:
- Total leave days
- American Psychiatric Association. 2022. APA Resource Document: Seclusion and Restraint. http://apapsy.ch/S-R
- American Psychiatric Nurses Association. 2022. APNA Standards of Practice: Seclusion and Restraint. https://www.apna.org/standards-of-practice-seclusion-and-restraint/
- Donat, D. (August, 2003). An analysis of successful efforts to reduce the use of seclusion and restraint at a public psychiatric hospital. Psychiatric Services. 54(8): 1119-1123.
- Fisher, W. A. (2003). Elements of successful restraint and seclusion reduction programs and their application in a large, urban, state psychiatric hospital. Journal of Psychiatric Practice, 9(1), 7-15.
- Huckshorn, K.A. (2004/September). Reducing seclusion and restraint use in mental health settings: Core strategies for prevention. Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services. 42(9). Pp. 22-31.
- Mohr, W. K., & Anderson, J. A. (2001). Faulty assumptions associated with the use of restraints with children. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing, 14(3), 141- 151.
- Special Section on Seclusion and Restraint, (2005, Sept). Psychiatric Services, 56 (9), 1104-1142.
- Success Stories and Ideas for Reducing Restraint/Seclusion. (2003). A compendium of strategies created by the American Psychiatric Association (APA), the American Psychiatric Nurses Association (APNA), the National Association of Psychiatric Health Systems (NAPHS), and the American Hospital Association Section for Psychiatric and Substance Abuse Services (AHA). Retrieved from the Internet on February 10, 2010 at http://www.naphs.org
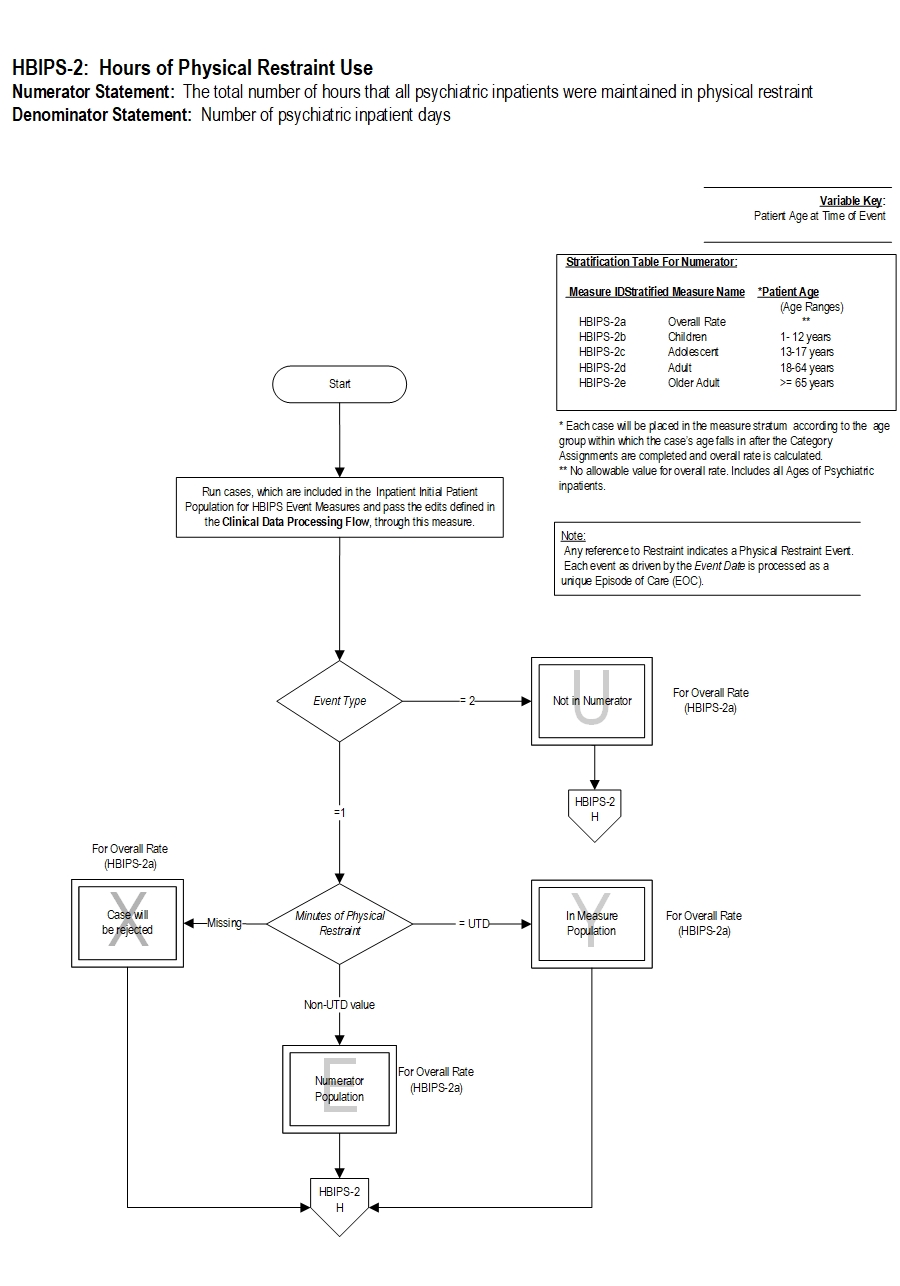

HBIPS-2: Hours of Physical Restraint Use
Algorithm Narrative
Numerator Statement: The total number of hours that all psychiatric inpatients were maintained in physical restraint
Denominator Statement: Number of psychiatric inpatient days
Variable key: Patient Age at Time of Event
Stratified Measure Name:
HBIPS-2a Overall Rate
HBIPS-2b Children1-12 years
HBIPS-2c Adolescent 13-17 years
HBIPS-2d Adult 18-64 years
HBIPS-2e Older Adult >=65 years
1. Run cases, which are included in the Inpatient Initial Patient Population for HBIPS Event Measures and pass the edits defined in the Clinical Data Processing Flow, through this measure.
2. Check Event Type
a. If Event Type equals 2, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of U for Overall Rate (HBIPS-2a) and will not be in the numerator population. Continue processing and proceed to step 4, check Overall Rate Category Assignment.
b. If Event Type equals 1, continue processing and proceed to Minutes of Physical Restraint.
3. Check Minutes of Physical Restraint
a. If Minutes of Physical Restraint is missing, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of X for Overall Rate (HBIPS-2a) and will be rejected. Continue processing and proceed to step 4, Initialize the Measure Category Assignment for each strata measure.
b. If Minutes of Physical Restraint equals UTD, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of Y for Overall Rate (HBIPS-2a) and will be in the measure population. Continue processing and proceed to step 4, Initialize the Measure Category Assignment for each strata measure.
c. If Minutes of Physical Restraint equals a Non-UTD Value , the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of E for Overall Rate (HBIPS-2a) and will be in the numerator population. Continue processing and proceed to step 4, Initialize the Measure Category Assignment for each strata measure.
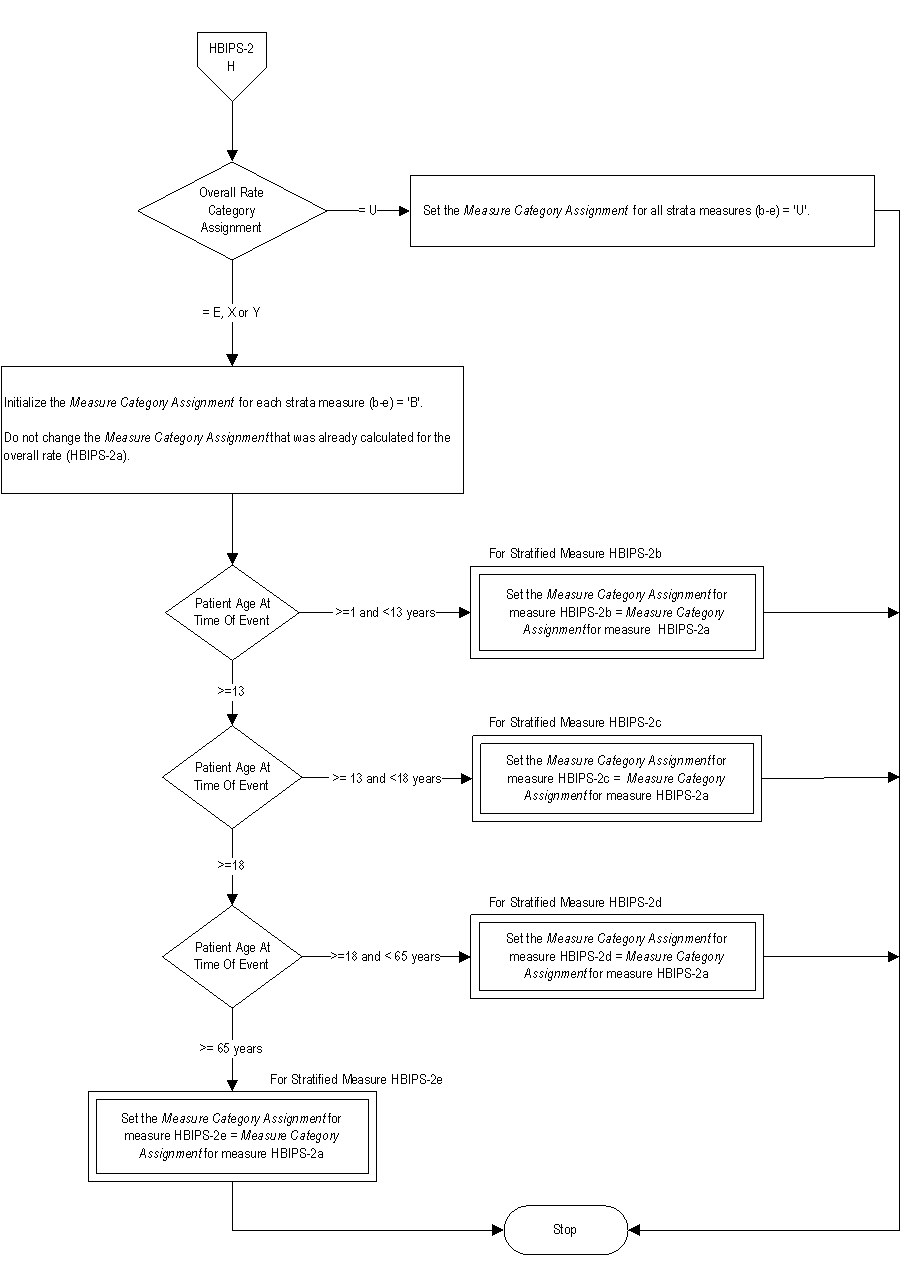
4. Check Overall Rate Category Assignment
a. If Overall Rate Category Assignment equals U, Set the Measure Category Assignment for all strata measures (b-e) = 'U'. Stop processing.
b. If Overall Rate Category Assignment equals E, X or Y , continue processing and Initialize the Measure Category Assignment for each strata measure (b-e) = ‘B’ . Do not change the Measure Category Assignment or Total Overall Restraint Minutes that was already calculated for the overall rate (HBIPS-2a).
5. Check Patient Age at Time of Event
a. If Patient Age at Time of Event is greater than or equal to 1 and less than 13 years, set the Measure Category Assignment for measure HBIPS-2b equal to Measure Category Assignment for measure HBIPS-2a. Stop processing.
b. If Patient Age at Time of Event is greater than or equal to 13 years, continue processing and proceed to Patient Age at Time of Event.
c. If Patient Age at Time of Event is greater than or equal to 13 and less than 18 years, set the Measure Category Assignment for measure HBIPS-2c equal to Measure Category Assignment for measure HBIPS-2a. Stop processing.
d. If Patient Age at Time of Event is greater than or equal to 18 years, continue processing and proceed to Patient Age at Time of Event.
e. If Patient Age at Time of Event is greater than or equal to 18 and less than 65 years, set the Measure Category Assignment for measure HBIPS-2d equal to Measure Category Assignment for measure HBIPS-2a. Stop processing.
f. If Patient Age at Time of Event is greater than or equal to 65 years, set the Measure Category Assignment for measure HBIPS-2e equal to Measure Category Assignment for measure HBIPS-2a. Stop processing.
Measure Calculation for Aggregated Denominator
Denominator: For the overall measure and each strata measure calculate the denominator rate by aggregating the Psychiatric Inpatient Days and Leave Days.
Number of Denominator Cases for the overall measure = (Psychiatric Inpatient Days – Leave Days), for all patients for the reporting month.
Number of Denominator Cases for each strata measure = (Psychiatric Inpatient Days – Leave Days), for all patients with a Patient Age (Reporting Date - Birthdate) appropriate for the strata for the reporting month where Reporting Date is the last date of the reporting month that the census data is being reported.
Performance Measurement Systems can refer to the Joint Commission’s ORYX Technical Implementation Guide for information concerning the aggregation of HCO level data, including the Observed Rate and Population Size for this measure.
CPT® only copyright 2024 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. CPT® is a registered trademark of the American Medical Association.
You, your employees and agents are authorized to use CPT® only as contained in The Joint Commission performance measures solely for your own personal use in directly participating in healthcare programs administered by The Joint Commission. You acknowledge that the American Medical Association (“AMA”) holds all copyright, trademark and other rights in CPT®.
Any use not authorized herein is prohibited, including by way of illustration and not by way of limitation, making copies of CPT® for resale and/or license, transferring copies of CPT® to any party not bound by this Agreement, creating any modified or derivative work of CPT®, or making any commercial use of CPT®. License to use CPT® for any use not authorized herein must be obtained through the American Medical Association, Intellectual Property Services, AMA Plaza, 330 North Wabash Avenue, Suite 39300, Chicago, Illinois 60611-5885. Applications are available at the American Medical Association Web site, www.ama- assn.org/go/cpt.
U.S. Government Rights This product includes CPT® which is commercial technical data, which was developed exclusively at private expense by the American Medical Association, 330 North Wabash Avenue, Chicago, Illinois 60611. The American Medical Association does not agree to license CPT® to the Federal Government based on the license in FAR 52.227-14 (Data Rights - General) and DFARS 252.227-7015 (Technical Data - Commercial Items) or any other license provision. The American Medical Association reserves all rights to approve any license with any Federal agency.
Disclaimer of Warranties and Liabilities. CPT® is provided “as is” without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the AMA, are not part of CPT®, and the (AMA is not recommending their use. The AMA does not directly or indirectly practice medicine or dispense medical services. The responsibility for the content of this product is with The Joint Commission, and no endorsement by the AMA is intended or implied. The AMA disclaims responsibility for any consequences or liability attributable to or related to any use, non-use, or interpretation of information contained or not contained in this product.
This Agreement will terminate upon notice if you violate its terms. The AMA is a third party beneficiary to this Agreement.
Should the foregoing terms and conditions be acceptable to you, please indicate your agreement and acceptance by clicking below on the button labeled “accept”.