Measure Information Form
Version 2023B
Measure Information Form
According to Glantz (2005), compared to spontaneous labor, elective inductions result in more cesarean births and longer maternal length of stay. Interventions that decrease the chance of a cesarean delivery include avoiding non–medically indicated induction of labor prior to 39 weeks gestation (Quinlan and Murphy, 2015). Repeat elective cesarean births before 39 weeks gestation also result in higher rates of adverse respiratory outcomes, mechanical ventilation, sepsis and hypoglycemia for the newborns (Tita et al., 2009).
Type Of Measure: Process Improvement Noted As: Decrease in the rateIncluded Populations: ICD-10-PCS Principal Procedure Code or ICD-10-PCS Other Procedure Codes for one or more of the following:Denominator Statement: Patients delivering newborns with >= 37 and < 39 weeks of gestation completedExcluded Populations: None Data Elements:
- Medical induction of labor as defined in Appendix A, Table 11.05 Medical Induction of Labor while not in Labor prior to the procedure
- Cesarean birth as defined in Appendix A, Table 11.06 Cesarean Birth and all of the following:
- not in Labor
- no history of a Prior Uterine Surgery
Included Populations:
- ICD-10-PCS Principal Procedure Code or ICD-10-PCS Other Procedure Codes for delivery as defined in Appendix A, Table 11.01.1 Delivery
Excluded Populations:
- ICD-10-CM Principal Diagnosis Code or ICD-10-CM Other Diagnosis Codes for planned cesarean birth in labor as defined in Appendix A, Table 11.06.1 Planned Cesarean Birth in Labor
Data Elements:
- ICD-10-CM Principal Diagnosis Code or ICD-10-CM Other Diagnosis Codes for conditions possibly justifying elective delivery prior to 39 weeks gestation as defined in Appendix A, Table 11.07 Conditions Possibly Justifying Elective Delivery
- History of prior stillbirth
- Less than 8 years of age
- Greater than or equal to 65 years of age
- Length of stay > 120 days
- Gestational Age < 37 or >= 39 weeks or UTD
- Borders, E.B., Birsner, M.L., Gyanmfi-Bannerbaum, C. (2019). Avoidance of nonmedically indicated early-term deliveries and associated neonatal morbidities. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee Opinion, 133:2, e156-163.
- Clark, S., Miller, D., Belfort, M., Dildy, G., Frye, D., & Meyers, J. (2009). Neonatal and maternal outcomes associated with elective delivery. [Electronic Version]. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 200:156.e1-156.e4.
- Glantz, J. (Apr.2005). Elective induction vs. spontaneous labor associations and outcomes. [Electronic Version]. J Reprod Med. 50(4):235-40.
- Kilpatrick, S. J., Papile, L.-A., & Macones, G. A. (Eds.). (2017). Guidelines for perinatal care (8th ed.). American Academy of Pediatrics.
- Tita, A., Landon, M., Spong, C., Lai, Y., Leveno, K., Varner, M, et al. (2009). Timing of elective repeat cesarean delivery at term and neonatal outcomes. [Electronic Version]. NEJM. 360:2, 111-120.
- Quinlan, J. D., & Murphy, N. J. (2015). Cesarean delivery: counseling issues and complication management. American family physician, 91(3), 178–184.
Hospital Corporation of America-Women's and Children's Clinical Services
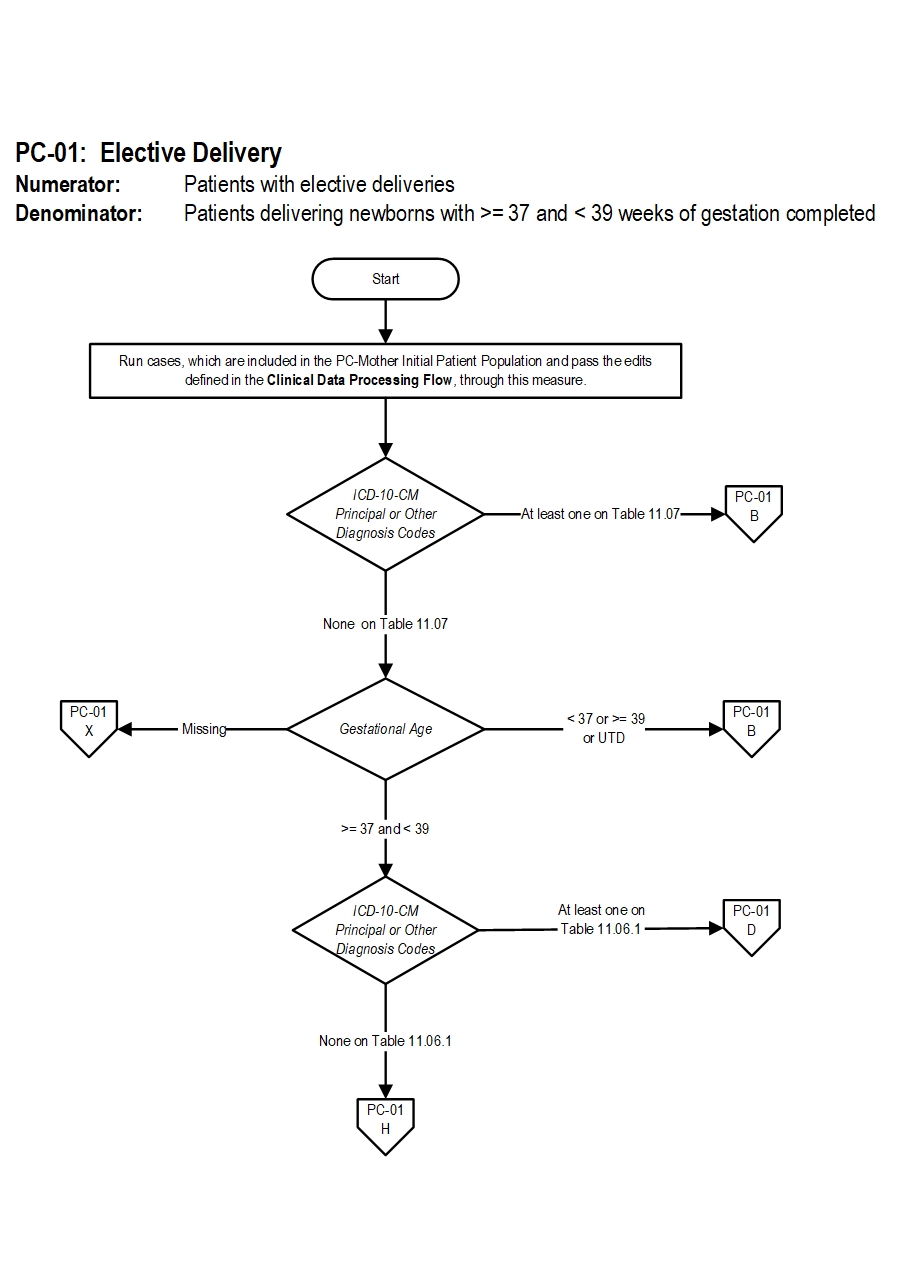
PC-01: Elective Delivery Algorithm Narrative
Numerator: Patients with elective deliveriesDenominator: Patients delivering newborns with >= 37 and < 39 weeks of gestation completed
Variable Key: Patient Age, Newborn Patient Age at Admission, Initial Patient Population Reject Case Flag and Length of Stay
1. Start processing. Run cases, which are included in the PC-Mother Initial Patient Population and pass the edits defined in the Clinical Data Processing Flow, through this measure.
2. Check ICD-10-CM Principal or Other Diagnosis Codes
- If at least one of the ICD-10-CM Principal or Other Diagnosis Codes is on Table 11.07, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of B and will not be in the Measure Population. Stop processing.
- If all ICD-10-CM Principal and Other Diagnosis Codes are missing or none of them on Table 11.07, continue processing and proceed to check Gestational Age.
- If Gestational Age is missing, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of X and will be rejected. Stop processing.
- If Gestational Age equals or greater than 37 and Less than 39, the case will proceed to check ICD-10-CM Principal or Other Diagnosis Codes
- If Gestational Age Less than 37 or equals or greater than 39 or is UTD, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of B and will not be in the Measure Population. Stop processing.
- If at least one of the ICD-10-CM Principal or Other Diagnosis Codes is on Table 11.06.1, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of D and will be in the population. Stop processing.
- If all ICD-10-CM Principal and Other Diagnosis Codes are missing or none of them on Table 11.06.1, continue processing and proceed to check ICD-10-PCS Principal or Other Procedure Codes.
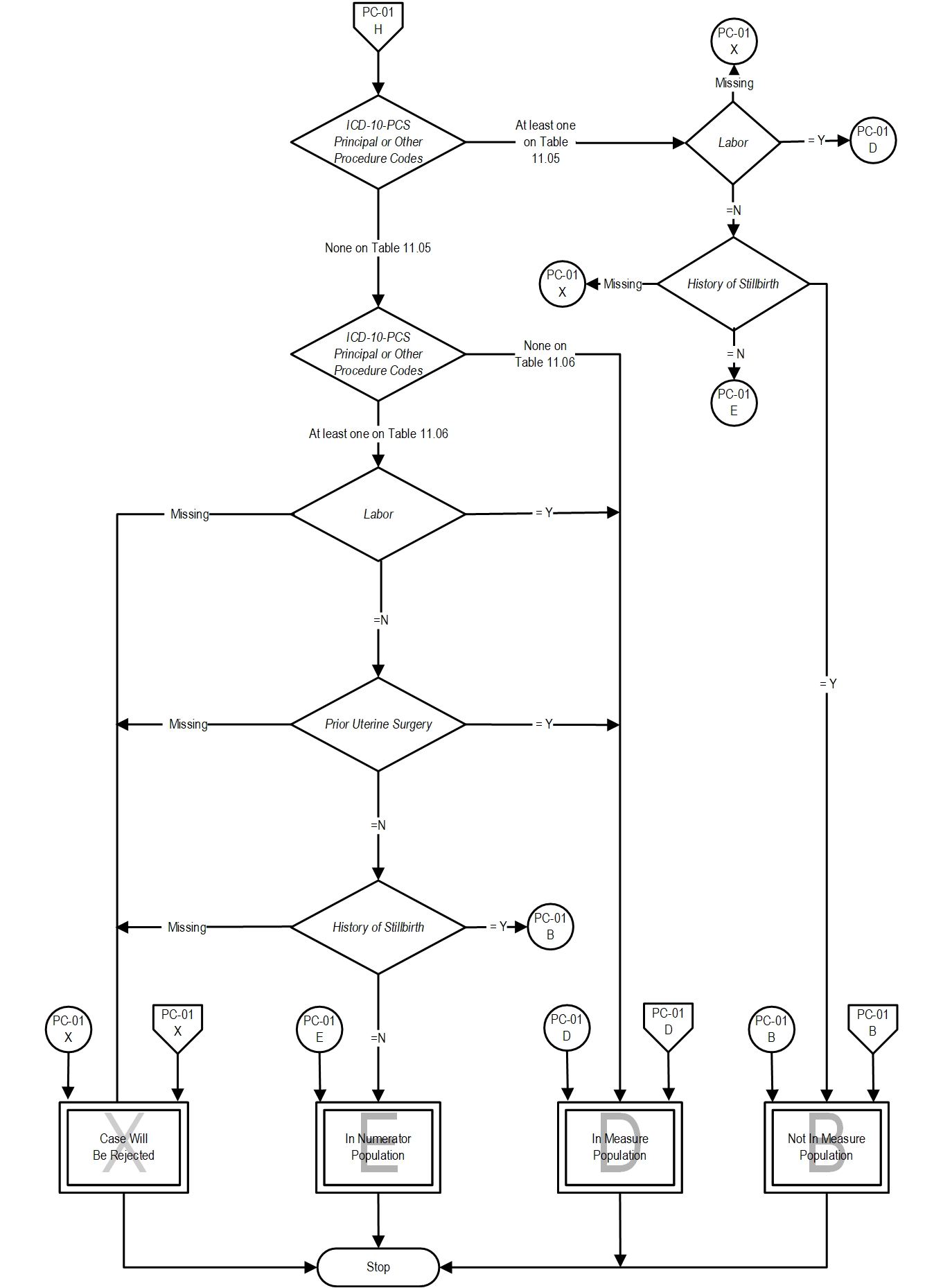
- If at least one of the ICD-10-PCS Principal or Other Procedure Codes is on Table 11.05, the case will proceed to step 10 check Labor.
- If all ICD-10-PCS Principal or Other Procedure Codes are missing or none of them on Table 11.05, continue processing and proceed to check ICD-10-PCS Principal or Other Procedure Codes
- If at least one of the ICD-10-PCS Principal or Other Procedure Codes is on Table 11.06 , the case will proceed to step 7 check Labor.
- If all ICD-10-PCS Principal or Other Procedure Codes are missing or none of them on Table 11.06, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of D and will be in the population. Stop processing.
- If Labor is missing, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of X and will be rejected. Stop processing.
- If Labor equals Y, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of D and will be in the population. Stop processing.
- If Labor equals N, continue processing and proceed to check Prior Uterine Surgery.
- If Prior Uterine Surgery is missing, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of X and will be rejected. Stop processing.
- If Prior Uterine Surgery equals Y, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of D and will be in the population. Stop processing.
- If Prior Uterine Surgery equals N, continue processing and proceed to check History of Stillbirth.
- If History of Stillbirth is missing, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of X and will be rejected. Stop processing.
- If History of Stillbirth equals Y, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of B and will not be in the Measure Population. Stop processing.
- If Prior Uterine Surgery equals N, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of E and will be in the numerator population.
- If Labor is missing, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of X and will be rejected. Stop processing.
- If Labor equals Y, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of D and will be in the population. Stop processing.
- If Labor equals N, continue processing and proceed to check History of Stillbirth.
- If History of Stillbirth is missing, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of X and will be rejected. Stop processing.
- If History of Stillbirth equals Y, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of B and will not be in the Measure Population. Stop processing.
- If Prior Uterine Surgery equals N, the case will proceed to a Measure Category Assignment of E and will be in the numerator population.
CPT® only copyright 2023 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. CPT® is a registered trademark of the American Medical Association.
You, your employees and agents are authorized to use CPT® only as contained in The Joint Commission performance measures solely for your own personal use in directly participating in healthcare programs administered by The Joint Commission. You acknowledge that the American Medical Association (“AMA”) holds all copyright, trademark and other rights in CPT®.
Any use not authorized herein is prohibited, including by way of illustration and not by way of limitation, making copies of CPT® for resale and/or license, transferring copies of CPT® to any party not bound by this Agreement, creating any modified or derivative work of CPT®, or making any commercial use of CPT®. License to use CPT® for any use not authorized herein must be obtained through the American Medical Association, Intellectual Property Services, AMA Plaza, 330 North Wabash Avenue, Suite 39300, Chicago, Illinois 60611-5885. Applications are available at the American Medical Association Web site, www.ama- assn.org/go/cpt.
U.S. Government Rights This product includes CPT® which is commercial technical data, which was developed exclusively at private expense by the American Medical Association, 330 North Wabash Avenue, Chicago, Illinois 60611. The American Medical Association does not agree to license CPT® to the Federal Government based on the license in FAR 52.227-14 (Data Rights - General) and DFARS 252.227-7015 (Technical Data - Commercial Items) or any other license provision. The American Medical Association reserves all rights to approve any license with any Federal agency.
Disclaimer of Warranties and Liabilities. CPT® is provided “as is” without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the AMA, are not part of CPT®, and the (AMA is not recommending their use. The AMA does not directly or indirectly practice medicine or dispense medical services. The responsibility for the content of this product is with The Joint Commission, and no endorsement by the AMA is intended or implied. The AMA disclaims responsibility for any consequences or liability attributable to or related to any use, non-use, or interpretation of information contained or not contained in this product.
This Agreement will terminate upon notice if you violate its terms. The AMA is a third party beneficiary to this Agreement.
Should the foregoing terms and conditions be acceptable to you, please indicate your agreement and acceptance by clicking below on the button labeled “accept”.