Measure Information Form
Version 2018B1
Measure Information Form
| Set Measure ID | Performance Measure Name |
|---|---|
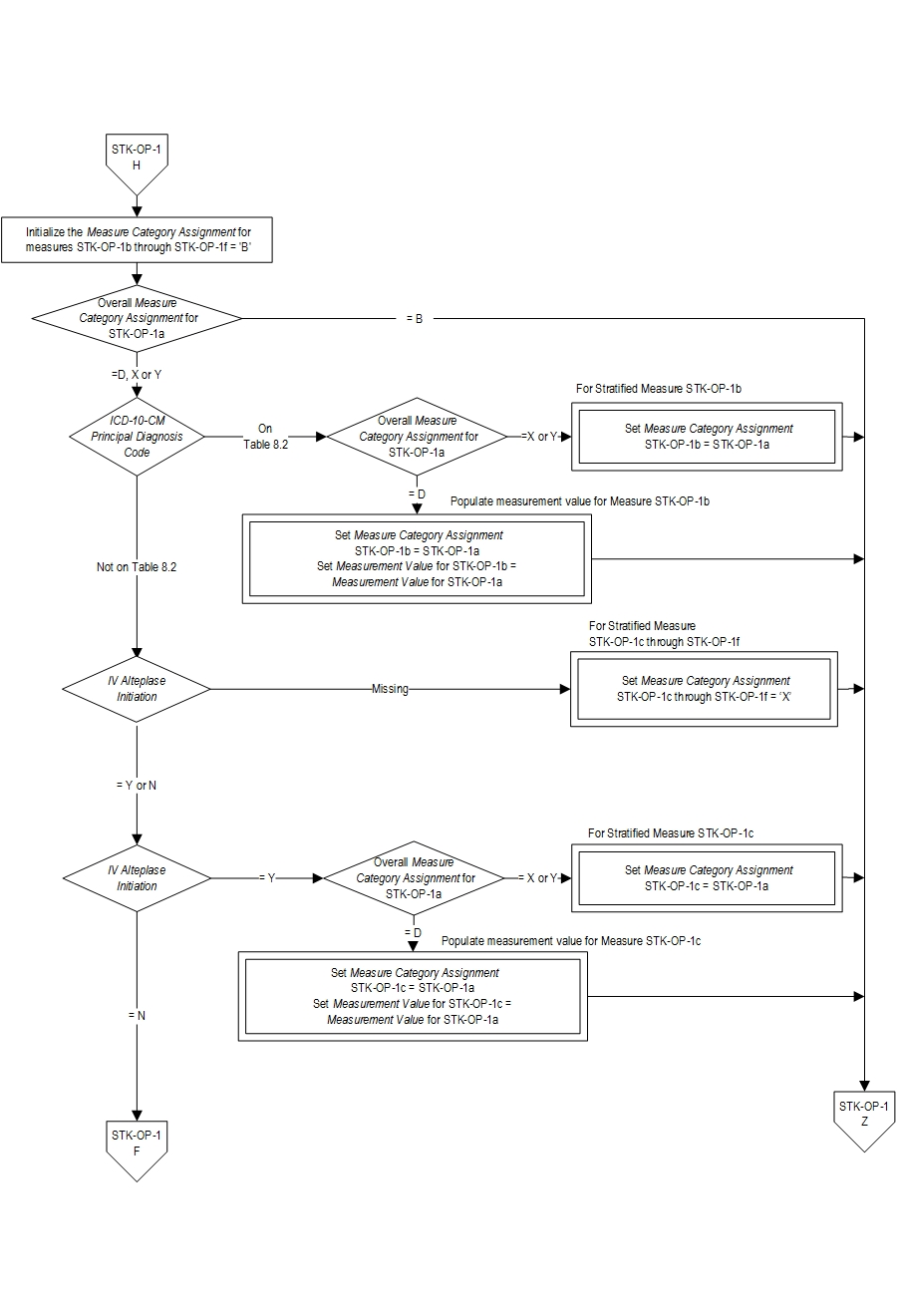
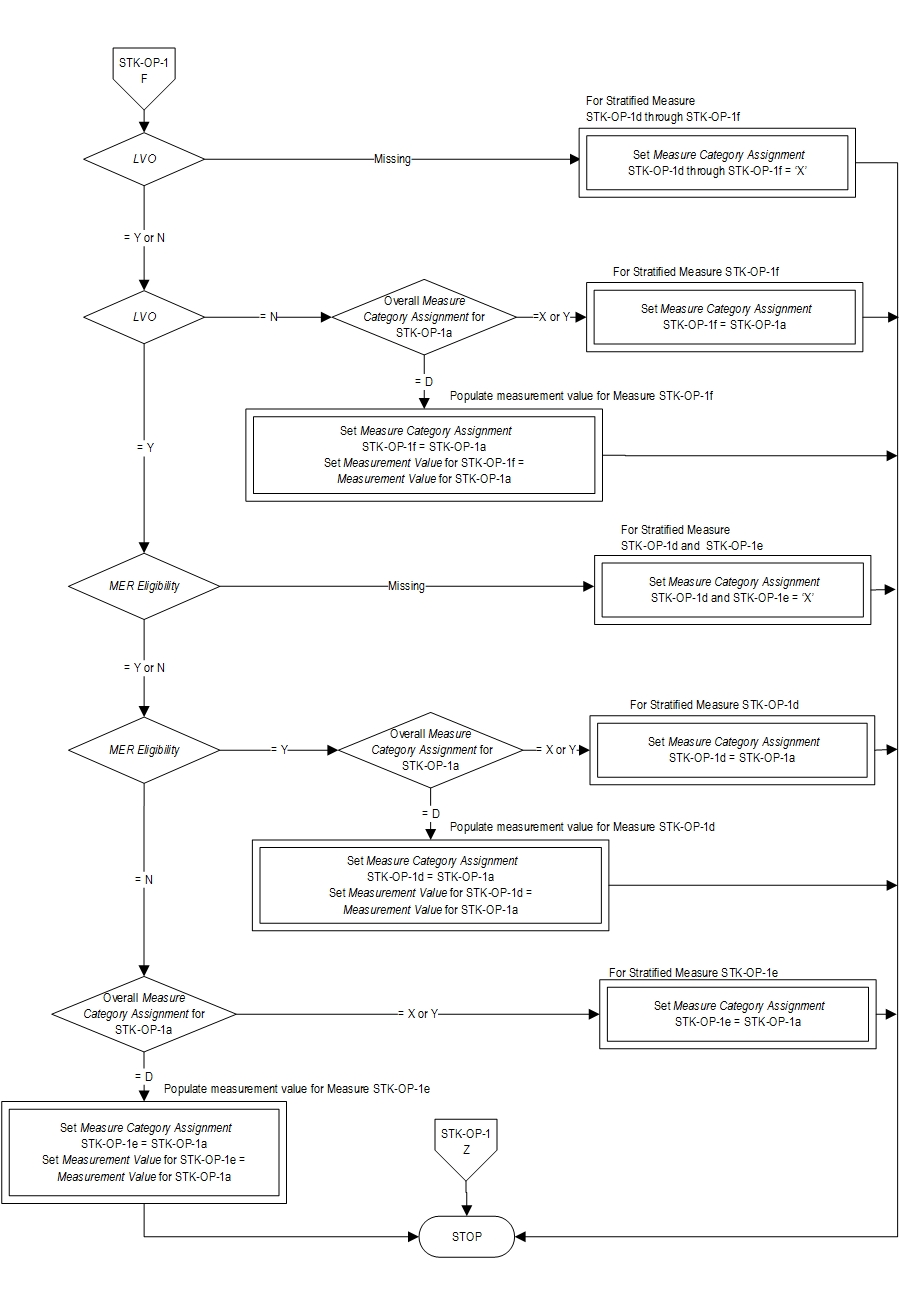
| STK-OP-1b | Hemorrhagic Stroke |
| STK-OP-1c | Ischemic Stroke; IV Alteplase Prior to Transfer (Drip and Ship) |
| STK-OP-1d | Ischemic Stroke; No IV Alteplase Prior to Transfer, LVO and MER Eligible |
| STK-OP-1e | Ischemic Stroke; No IV Alteplase Prior to Transfer, LVO and NOT MER Eligible |
| STK-OP-1f | Ischemic Stroke; No IV Alteplase Prior to Transfer, No LVO |
| STK-OP-1a | Overall Rate (Not Reported) |
The benefits of both IV altelplase and mechanical thrombectomy for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke are time dependent. The earlier the treatment within the time window, the greater the benefit to patients. Initiation of IV alteplase at a primary stroke center (PSC) and rapid transport to an advanced center capable of performing endovascular treatment may lead to faster and more complete reperfusion for certain patients eligible for these treatments (Powers, 2018).
The Brain Attack Coalition recommends that such transfers occur within 2 hours of patient arrival at the transferring stroke center (Alberts, 2013). Reducing the time stroke patients remain in the emergency department (ED) can improve access to a higher-level of stroke care and surgical intervention or advanced intra-arterial endovascular treatments, and increase quality of care. For those stroke patients who are not transferred to a TSC or CSC, inpatient admission within 3 hours, preferably to a formal stroke unit, is recommended (Jauch, 2013).
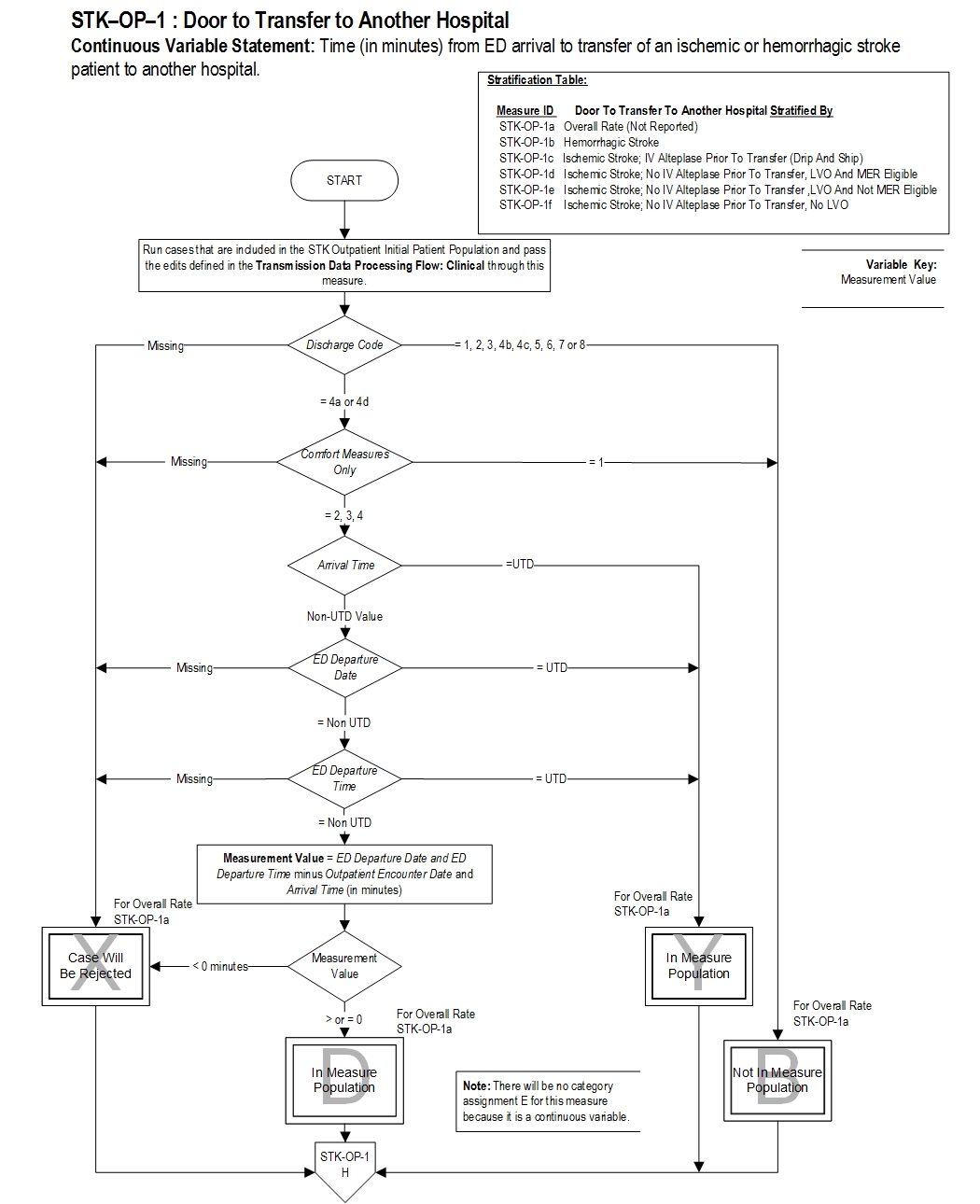
Type Of Measure: Process Improvement Noted As: Decrease in the median valueSTK-OP-1b Time (in minutes) from ED arrival to transfer of a hemorrhagic stroke patient to another hospital
STK-OP-1c Time (in minutes) from ED arrival to transfer of an ischemic stroke patient (drip and ship) to another hospital
STK-OP-1d Time (in minutes) from ED arrival to transfer of an ischemic stroke patient (no IV t-PA prior to transfer, LVO and MER eligible) to another hospital
STK-OP-1e Time (in minutes) from ED arrival to transfer of an ischemic stroke patient (no IV t-PA given prior to transfer, LVO and not MER eligible) to another hospital
STK-OP-1f Time (in minutes) from ED arrival to transfer of an ischemic stroke patient (no IV t-PA given prior to transfer, no LVO) to another hospital
Included Populations:Risk Adjustment: No. Data Collection Approach: Retrospective data sources for required data elements include administrative data and medical records. Some hospitals may prefer to gather data concurrently by identifying patients in the population of interest. This approach provides opportunities for improvement at the point of care/service. However, complete documentation includes the principal or other ICD-10 diagnosis and procedure codes, which require retrospective data entry. Data Accuracy: Variation may exist in the assignment of ICD-10 codes; therefore, coding practices may require evaluation to ensure consistency. Measure Analysis Suggestions: None Sampling: No. Data Reported As: Aggregate measure of central tendency . Selected References:AND
- Patients with an ICD-10-CM Principal Diagnosis Code for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke as defined in Appendix A, Table 8.1 or Table 8.2
AND
- Patients who are transferred to another hospital
Excluded Populations:
- An E/M Code for emergency department encounter as defined in Appendix A, Table 1.0
Data Elements:
- Patients less than 18 years of age
- Patients with Comfort Measures Only documented on day of or day after arrival
- Patients who expired in the emergency department
- Discharges to dispositions other than an acute care facility
- Alberts MJ, Wechsler LR, Jensen MEL, Lachtaw RE, Crocco TJ, George MG, Baranski J, Bass RR, et al. “Formation and Function of Acute Stroke-Ready Hospitals Within a Stroke System of Care Recommendations From the Brain Attack Coalition” [In Eng]. Stroke (Nov 12 2013).
- Albright KC, Branas CC, Meyer BC, Matherne-Meyer DE, Zivin JA, Lyden PD, Carr BG. “Acute Cerebrovascular Care in Emergency Stroke Systems.” [In Eng]. Arch Neurol (Oct 2010).
- American Heart Association. Acute Stroke Ready Hospital, 2015.
- Jauch, E. C., J. L. Saver, H. P. Adams, Jr., A. Bruno, J. J. Connors, B. M. Demaerschalk, P. Khatri, et al. "Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association." [In Eng]. Stroke (Jan 31 2013).
- Lyerly MJ, Albright KC, Boehme AK, Shahripour RB, Donnelly JP, Houston JT, Rawal PV, Kapoor N, Alvi M, Sisson A, Alexandrov AW, Alexandrov AV. “Patient Selection for Drip and Ship Thrombolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke”. [In Eng]. South Med J (Jul 2015).
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, Biller J, et al; on behalf of the American Heart Association Stroke Council. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018 Jan;49:e8, e10.
- Sheth KN, Smith EE, Grau-Sepulveda MV, Kleindorfer D, Fonarow GC, Schwamm LH. "Drip and Ship Thrombolytic Therapy for Acute Ischemic Stroke: Use, Temporal Trends, and Outcomes.” [In Eng]. Stoke (Mar 2015).